Abstract
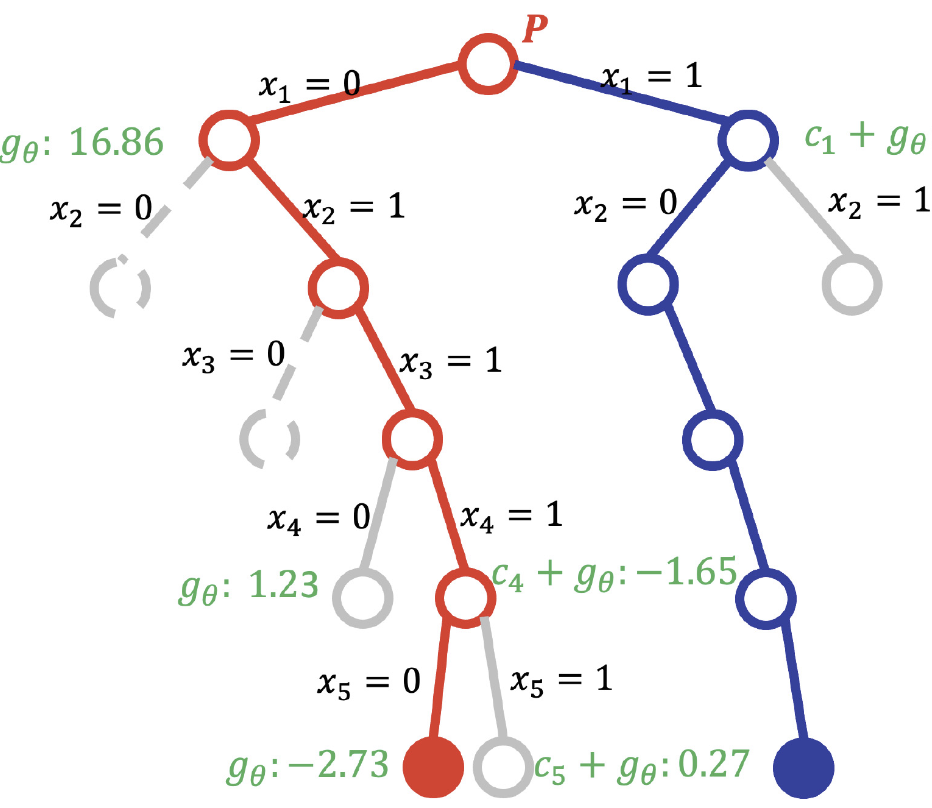
Algorithm design is an art that heavily requires human designers’ intuition, expertise, and insights into the combinatorial structure of the problems under consideration. In particular, while greedy algorithms for NP-complete problems are generally straightforward, finding an effective greedy-selection rule is consistently challenging. In the study, we introduce an approach called artificial intelligence algorithmist for set cover problem (AIA-SC), which leverages neural networks as greedy-selection rules to solve the minimum weighted set cover problem (WSCP), an NP-complete problem. Initially, we formulate a given WSCP as a 0–1 integer linear program (ILP), in which each variable is binary: indicating the exclusion of set , and indicating the selection of the set. Subsequently, we design a generic search framework to identify the optimal solution to the ILP. At each search step, the value of a variable is determined with the aid of neural networks. The key ingredients of our neural network involve the design of its loss function and training process: the original ILP problem and the sub-problems generated by assigning a variable should satisfy the Bellman-Ford equation, which enables us to set the violation of Bellman-Ford equation as loss function of our neural network. Experimental results on representative instances indicate that the neural network-based greedy selection rule effectively identifies optimal solutions and surpasses the performance of the human-crafted Chvatal’s greedy algorithm. Furthermore, the basic idea of our approach can be readily extended to design greedy algorithms for other NP-hard problems without significant modification. The source code of AIA-SC and data sets are available at https://github.com/zxding94/aia-sc.