Abstract
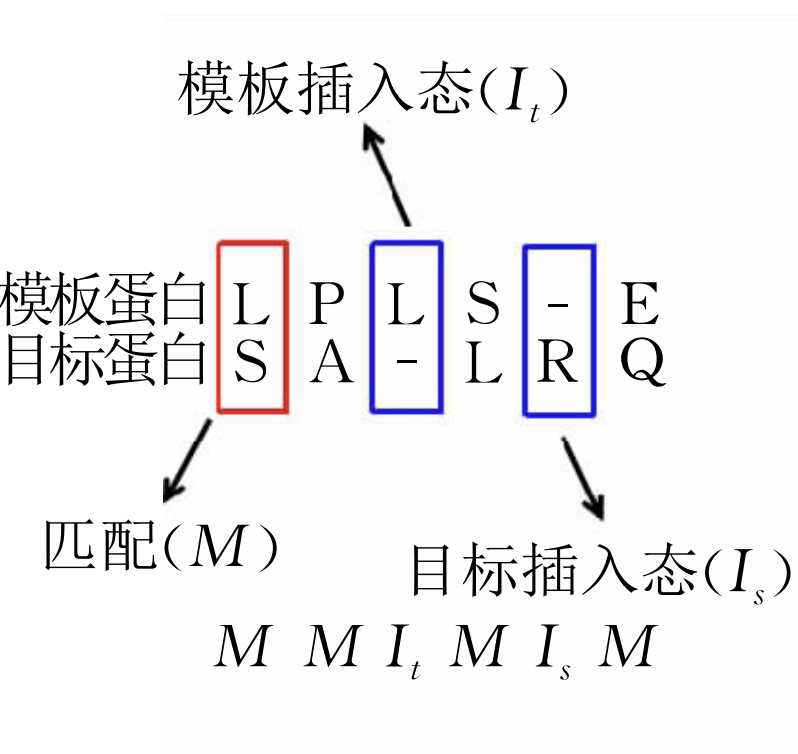
Proteins are important macromolecules that consist of one or more long chains of amino acids,and perform a great variety of biological functionalities,including catalyzing, transportation,and responses to stimuli.In natural environment,aprotein usually folds into a specific tertiary structural conformation called native structure.The functionalities of a protein are largely determined by its structural conformation,rending the understanding of protein structures fatally important.However,the experimental approaches for the determination of protein structures are commonly labor-intensive and time-consuming,and thus cannot match up the speed of protein sequencing.Therefore,it is invaluable to predict protein structures using computational approaches.In this study,we summarized the popular strategies for protein structure prediction,including homology modeling approaches based on sequence-sequence alignment,threading approaches based on sequence-structure alignment,and ab initio approaches based on optimizing energy functions.Furthermore,we listed the popular software packages for protein structure prediction as well as their performance in the CASP(Critical Assessment of protein Structure Prediction)competition.The evaluation of these approaches showed the following three observations:(1)If the sequence identity between a query protein and a certain template protein exceeds 30%,homology modeling approaches usually report accurate prediction results; (2)For threading approaches,how to improve fold recognition for remote homology proteins remains one of the challenges;and(3)For ab initio approaches,the design of an accurate energy function,together with building structural conformation with the assistance of the information of residue-residue contact information still need investigation.Finally,we summarized this study by listing our perspectives on protein structure prediction,especially on the the perspective that protein folding is an elite-driven process.Specifically,the correlation between protein sequence and its native structure is not that strong from the global point of view;however,at certain regions,local sequences carry strong signals of local structural preference.These regions might initialize the protein folding process,and speed up protein folding through significantly reducing search space of possible structural conformations.The understanding of these regions should greatly facilitate the developing of novel approaches for protein structure prediction.In summary, the accurate prediction of protein structures heavily relies on our insights into the relationship between protein sequence and structure,as well as modeling these insights into an efficient statistical models and algorithms.Protein structure is a representative problem that a linear sequence of entities forms specific complex structures under the interactions among these entities; thus,the advances in the field of protein structure prediction will contribute to solving other similar problems.